
Solution :
Que : 01

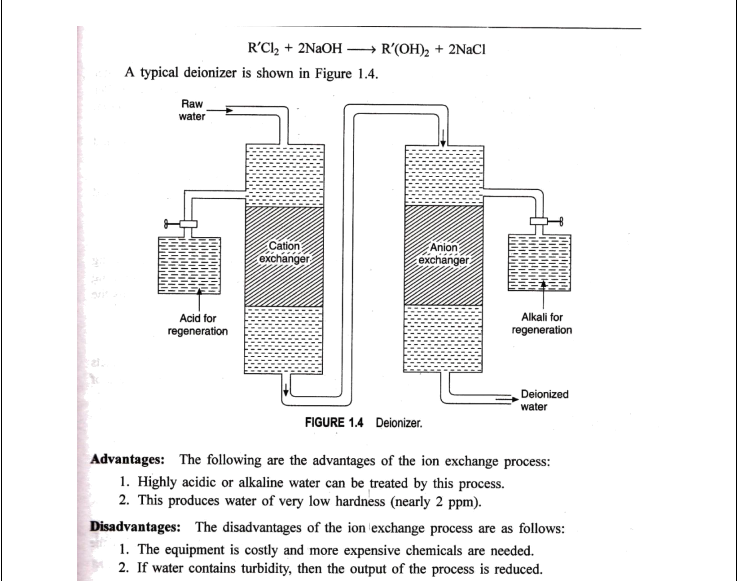
Que : 02

Que 3: What are the essential requirements of boiler feed water? Discuss the boiler problems due to using impure water in detail.
Ans: Boiler feedwater is the water that is supplied to a boiler for generating steam. The quality of the feedwater plays a critical role in ensuring the efficient and safe operation of the boiler. The essential requirements of boiler feedwater are as follows:
- Purity: Boiler feedwater should be free from impurities such as suspended solids, dissolved minerals, organic matter, and gases. The presence of impurities can cause scale formation, corrosion, and fouling, leading to reduced efficiency and safety hazards.
- pH: The pH of the feedwater should be within a specific range to prevent corrosion and scale formation. Typically, the pH range for boiler feedwater is between 8.5 and 9.5.
- Hardness: Hardness in water is caused by the presence of dissolved minerals such as calcium and magnesium. Hardness can cause scaling in the boiler, reducing its efficiency. The recommended maximum hardness for feedwater is 0.2 parts per million (ppm) as calcium carbonate.
- Alkalinity: Alkalinity is the capacity of water to neutralize acids. High alkalinity in boiler feedwater can lead to the formation of scale and foaming. The recommended maximum alkalinity is 700 ppm as calcium carbonate.
- Oxygen: Oxygen in boiler feedwater can cause corrosion of metal surfaces. The recommended maximum oxygen concentration is 0.007 ppm.
Que 4: 0.5g of CaCO3 was dissolved in dil. HCL and then diluted up to 250 ml. 50ml of this solution requires 50ml of EDTA solution for titration. 50ml of hard water sample require 25 ml same EDTA solution for titration. 50ml of same hard water sample on boiling and filtering consumed 15ml of EDTA for titration. Calculate total, carbonate and non-carbonate hardness.
Ans: 0.5g of CaCO3 was dissolved in dil. HCL and then diluted up to 250 ml
Concentration of sample of hard water = 0.5g/250ml caco3
= 0.002g/ml = 2mg/ml
Now, 50ml of same hard water sample required 50ml EDTA.
1ml EDTA Solution = 50/50= 1ml CaCO3
Equivalent Hardness
Now, 50ml water sample = 25ml EDTA
Hardness of sample = 25*(50/50) mg CaCo3
= 25 mg CaCo3
Hardness per litre of sample = 25*(50/50)*1000 mg/l
= 500 mg/l
50 ml water sample after boiling = 15ml EDTA solution
Permanant 1 non carbonate hardness of sample = 15*(50/50) mg CaCo3
= 15 mg CaCo3
Permanant hardness of one liter = 15*(1000/50) mg CaCo3
= 300 mg/l of CaCo3
Temporary hardness = Total – permanent
= 500 – 300
= 200 mg/l of CaCo3
Que 5 : Define: Hard water, Soft water, Caustic embrittlement, Scale & Sludge.
Ans: Hard water : Hard water is a term that denotes water having a very high mineral content (the term is the opposite of ‘soft water’). As water percolates into deposits of calcareous, gypsum or chalk that are primarily composed of carbonates of magnesium or calcium, bicarbonate and sulphates, hard water is formed.
Soft wate r: Soft water can be defined as surface water that contains relatively low ion concentrations and is low in calcium and magnesium ions. Soft water naturally occurs where rough, impermeable and calcium-poor rocks are responsible for the formation of the runoff and the drainage basin of rivers.
Caustic embrittlement : Caustic embrittlement is a phenomenon that occurs in boilers where caustic substances accumulate in boiler materials. It also can be described as the cracking of riveted mild steel boiler plates. This occurs at temperatures of 200°-250°C as a result of local deposition of concentrated hydroxide.
Scale : Scale is hard mineral coatings and corrosion deposits made up of solids and sediments that collect on or in distribution system piping, storage reservoirs and household plumbing.
Sludge : Sludge is a water-formed sedimentary deposit which may include all suspended solids carried by the water and trace elements in solution in the water.