

Q1)
(A)(I) Explain Product Development Process.
Ans: Product development process refers to the series of steps that companies follow to create new products or services and bring them to market. The process typically involves several stages, each with its own set of objectives, activities, and outputs. Here’s a general overview of the typical product development process:
1)Idea Generation: This stage involves coming up with new product ideas, which can be generated through market research, customer feedback, or brainstorming sessions. The goal is to identify potential products that meet customer needs and align with the company’s strategic goals.
2)Concept Development: In this stage, the company develops a concept for the product based on the ideas generated in the previous stage. The concept typically includes the product’s features, benefits, target market, and value proposition. This stage involves researching and analyzing the feasibility of the product idea.
3)Design and Prototyping: Once the concept is developed, the company creates a design for the product and produces a prototype. The prototype can be used to test the product’s functionality, usability, and performance. This stage may involve multiple iterations of design and testing.
4)Testing and Validation: In this stage, the company tests the prototype and gathers feedback from customers and stakeholders. The goal is to validate the product’s performance, identify any potential issues, and make improvements as necessary.
5)Launch: Once the product is tested and validated, the company can launch it in the market. This stage involves creating a marketing plan, setting pricing and distribution strategies, and developing sales channels.
6)Post-Launch Evaluation: After the product is launched, the company monitors its performance, gathers customer feedback, and makes improvements as necessary. This stage involves continuous evaluation and improvement of the product to ensure its success in the market.
(II) Explain Product Development Process.
Ans: Product development process refers to the series of steps that companies follow to create new products or services and bring them to market. The process typically involves several stages, each with its own set of objectives, activities, and outputs. Here’s a general overview of the typical product development process:
1)Idea Generation: This stage involves coming up with new product ideas, which can be generated through market research, customer feedback, or brainstorming sessions. The goal is to identify potential products that meet customer needs and align with the company’s strategic goals.
2)Concept Development: In this stage, the company develops a concept for the product based on the ideas generated in the previous stage. The concept typically includes the product’s features, benefits, target market, and value proposition. This stage involves researching and analyzing the feasibility of the product idea.
3)Design and Prototyping: Once the concept is developed, the company creates a design for the product and produces a prototype. The prototype can be used to test the product’s functionality, usability, and performance. This stage may involve multiple iterations of design and testing.
4)Testing and Validation: In this stage, the company tests the prototype and gathers feedback from customers and stakeholders. The goal is to validate the product’s performance, identify any potential issues, and make improvements as necessary.
5)Launch: Once the product is tested and validated, the company can launch it in the market. This stage involves creating a marketing plan, setting pricing and distribution strategies, and developing sales channels.
6)Post-Launch Evaluation: After the product is launched, the company monitors its performance, gathers customer feedback, and makes improvements as necessary. This stage involves continuous evaluation and improvement of the product to ensure its success in the market.
(B)(I)
(II) Explain Design thinking as an effective problem solving approach.
Ans: The design thinking process is a problem-solving design methodology that helps you tackle complex problems by framing the issue in a human-centric way. The design thinking process works especially well for problems that are not clearly defined or have a more ambiguous goal.
Q2
(A) (I)Quality Function Deployment (QFD) is a customer-driven design process used to ensure that a product or service meets customer needs and expectations. The process involves identifying and prioritizing customer needs, translating them into technical requirements, and developing a product or service that meets those requirements. QFD uses matrices and diagrams to visually represent the relationship between customer needs, technical requirements, and design solutions. The process encourages cross-functional collaboration and continuous improvement to ensure that the product or service is of the highest quality.
(II)
(B) Enlist various steps involved in Design process and explain in brief
ANS> The various steps involved in the design process are Research, Ideation, Concept Development, Prototyping, Testing, and Implementation. Research involves gathering data and insights to understand the problem and user needs. Ideation involves generating and refining ideas for solutions. Concept Development involves creating a detailed plan for the chosen solution. Prototyping helps to create a low-fidelity version of the solution to test and refine it. Testing involves gathering feedback from users to refine the solution. Implementation involves bringing the solution to market. These steps help designers to create effective solutions that meet user needs and expectations.
Q3)
(A)(I)
(II)
(B)(I)
(II)
Q4
(A)
ANS>> Patent: A Patent is a set of exclusive rights granted by. a sovereign state or intergovernmental organization to an inventor or assignee for a limited period of time in exchange for detailed public disclosure of an invention.
(B) Define optimization. Explain the ways in which a design can be optimised.
Ans: Design optimization is a programmed mathematical technique that integrates this iterative design cycle in an automated process.
The analysis, evaluation, and modification tasks are performed automatically, making it possible to obtain an”optimum” design more efficiently.
Q5)
(A)
(B)
(C)
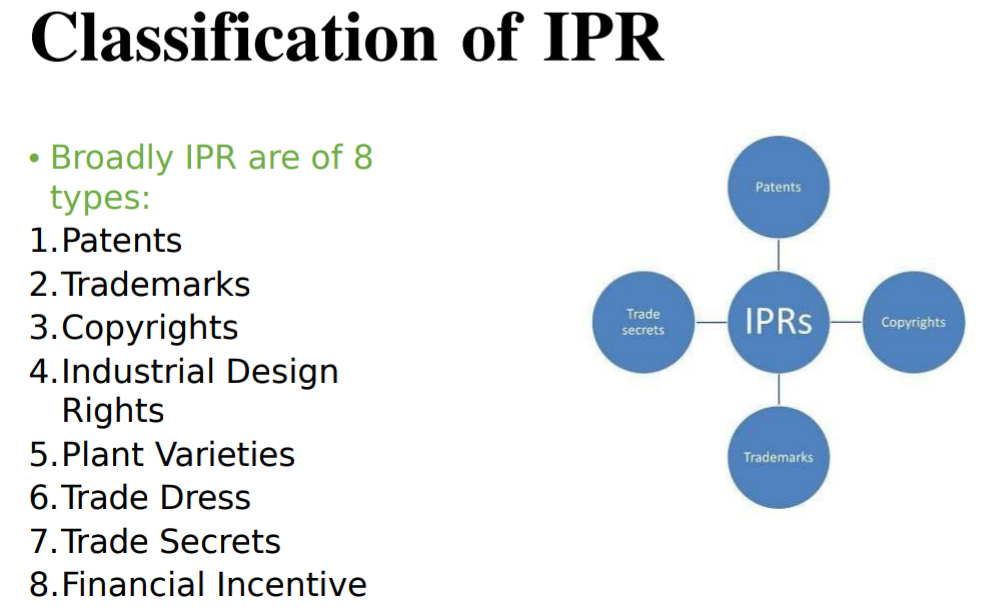
(D) Describe and classify Intellectual Property (IP).
Ans: Intellectual property refers to creations of the mind. It can be an invention (patent / utility model), a design (industrial design), a brand name (trademark, or a literary and artistic work (copyright).
Intellectual property rights are the rights given to persons over the creations of their minds.
It is a combination of science and technology.
It is given for any new creation such as composition of music, writing of a book, new invention.
(E)
| Trademark | Trade secret |
| A logo or graphical representation to differentiate one product or service from another | A secret or concept of any business that gives it an economic advantage over its competitors |
| Obtained by filing an application and registering the trademark | Obtained by keeping the information confidential and taking reasonable steps to prevent unauthorized disclosure |
| Lasts as long as the trademark is used and renewed periodically | Lasts as long as the information remains secret and valuable |
| Protects the identity and goodwill of a product or service from confusion or dilution | Protects the know-how, formulas, processes, designs or other information that is not publicly known |
| Can be enforced against anyone who infringes or misuses the trademark without permission | Can be enforced against anyone who acquires, uses or discloses the trade secret in a dishonest or unfair manner |
(F) Identify the concept of modular design by stating its advantages & disadvantages.
Ans: A modular design is an approach for product designing which is used to produce a complete product by integrating or combining smaller parts that are independent of each other. With the modular design approach, a complex product.